"Nat" in simple words !
In summary NAT has one important goal : Extend IP address space by translate private IP address to public IP address .
Obviously remember that IP ver 4 is not enough to use for anyone who want connect to internet .so its important to manage the use of IP address in the world by any way to prevent wasting IP addresses.
Network engineers in the world define 3 standards to manage IP address for avoid IP Address wasting :
- CIDR(Classless Inter domain Routing )
- Private addressing
- NAT
Memorize these notes for NAT :
- NAT technique that use IP v4 address through a public-to-private .
- NAT hide your network from Internet view.
- NAT is configured on a device such as router on edge between private network and public network (Internet )
- Because of NAT typically resides in a boundry router between private and public network cant function with "IP sec" ( the popular encryption technology for VPN . because IP sec requires trace end to end handshaking in other to setup initial encryption rules . and IP sec packets can't be modified or recognized by NAT )
- NAT = translate private IP address (invalid) to public IP address(valid) .
- NAT build NAT-table , a heart of nat working .if any connection is disconnected the registered field is removed from NAT-table .
- Any NAT process need 160 bytes memory . so if 1000 nat process occurred , means NAT need 1.6 Mb of memory .
- Because of connecting to internet using only a registered network number .
Ok ! lets talk about " How NAT works ?"
NAT resides in a router in edge of your network and internet . below figures show how NAT do and how NAT-table is complete.
- In cisco terminology NAT devide network in 2 parts. Inside and Outside. each of them have two sides . local and global . you can see them in below figures .
- Inside Local : Your private IP address and Hosts in your network , all of them inn inside local.
- Outside Local : Default gateway IP address .(Routers interface that connected to your LAN)
- Inside Global : routers interface public IP address that connected to internet .
- Outside Global : Public IP address of internet .
- Actually NAT translate inside local IP address to outside global IP address by changing source and destination IP address in received packets.

NAT works in 3 terms :
- Static NAT :
- one-to-one mapping address between inside local and inside global . for example one host need to connect to internet and a router do that by map its private IP to public IP address.
- for each connected device in NAT-table a new record is registered and if disconnected the record is removed .
- In static NAT if more than one private IP address need to connect to internet in needs the same quantity public IP address . (This is a big problem for static NAT )
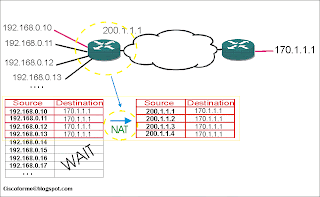
- Look at below figure :

- in this picture as you see for each private ip Address need same as quantity public IP address . imagine that if hundreds of hosts want toi connect internet how much public ip address we need ? is it possible?!..
2. Dynamic NAT :
- Dynamic NAT have some difference from static NAT . both of them mapping private-to-public IP address (or reverse). but dynamic NAT setup a pool of possible inside global IP address that match with any request to router to connect to internet .
- NAT can be configured with more IP addresses in the inside local address list than in the
inside global address pool. The router allocates addresses from the pool until all are
allocated. If a new packet arrives from yet another inside host, and it needs a NAT entry, but all the pooled IP addresses are in use, the router simply discards the packet. The user must try again until a NAT entry times out, at which point the NAT function works for the next host that sends a packet. Essentially, the inside global pool of addresses needs to be as large as the maximum number of concurrent hosts that need to use the Internet at the - same time—unless you use PAT, as is explained in the next section
- you can manually clear the table with this statement : #clear ip nat tranlateion
3.Overloading NAT by PAT (Port address translation)
- as you see in real world if hundreds or thouseneds of hosts need to communicate with internet last 2 kind of NAT don't useful. and another way is necessary .
- PAT solves the nat overlapping and allows NAT to scale to suport many clients with only a few public ip address.
- with PAT router can accept all of request and do like this : make a packet with source address of inside global IP-address with differenet port numbers for different host IPs (local inside IP-address)
- because of each port need 16 bits so can use more than 65000 port .
- the dynamic entry still in the table as traffic flows occasionally.
- When PAT creates the dynamic mapping it selects not only an inside global address but also a unique port number to use with that address .
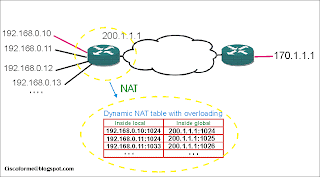
- actually both of Static and dynamic NAT translate one-to-one mapping in other side PAT use port numbers and significantly reduce the number of required registered ip address .
- if one company uses public IP addresses instead of private ip address then this company with thease ip address to conncting internet have some problems. because of using public ip addrees that means these ip addresses sets more then one once.
- in below figure as you can see hosts in inside network uses IP addresses with network of 170.1.1.0/24 . so if host A want to ping or send a request to cisco.com , the request is sent to router then router forward it to 170.1.1.1 a host in that LAN. to solve this problem we should config Overlapping NAT on router . so router can mapping source and destination IP address . how ? first host A send a DNS request for cisco.com NAT router resolve DNS request and maps cisco.com ip address (170.1.1.1) with outside local IP address of his E0/0 ip address , 192.168.0.1 . then host A thoughts that the cisco.com ip address is 192.168.0.1 and send his all request to this ip address. look at below figure to NAT table to better understanding .

NAT Configuration :
Static NAT Configuration :
1. On interface that connect to LAN (Local outside interface ) : #ip nat inside
2. On interface that connect to WAN (Global inside interface ) : #ip nat outside
3. # ip nat inside source static private-address public-address
R1(config)#ip nat inside source static 192.168.0.10 85.198.0.1
4. # ip nat inside source static port private-address port-number public-address port-number
R1(config) #ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.0.4 25 85.198.0.1 25
R1(config)#ip nat inside source static udp 192.168.0.1 53 85.198.0.1 53
5. #show ip nat statics :
R1#show ip nat statistics
Total active translations: 3 (3 static, 0 dynamic; 2 extended)
Outside interfaces:
FastEthernet0/1
Inside interfaces:
FastEthernet0/0
Hits: 0 Misses: 0
Expired translations: 0
Dynamic mappings:
6. #show ip nat translation :
R1#show ip nat translations
Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
--- 85.198.0.1 192.168.0.10 --- ---
Tcp 85.198.0.1:25 192.168.0.4:25 --- ---
udp 85.198.0.1:53 192.168.0.1:53 --- ---
Dynamic NAT Configuration :
1. On interface that connect to LAN (Local outside interface ) : #ip nat inside
2. On interface that connect to WAN (Global inside interface ) : #ip nat outside
3. Making pool on inside global interface of router :
#ip nat pool pool-name start-network end-network netmask
Router(config)#ip nat pool network1 85.198.0.1 85.198.0.5 netmask 255.255.255.248
4. Making access-list to make a a list of allowable ip-address to access internet :
#access-list statndard-no permit network wildcard-mask
Router(config)#access-list 50 permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255
5. #ip nat inside source list access-list-no pool pool-name
Router(config)#ip nat inside source list 50 pool network1
7. #show ip nat statics :
Router#show ip nat statistics
Total active translations: 0 (0 static, 0 dynamic; 0 extended)
Outside interfaces:
FastEthernet0/0
Inside interfaces:
FastEthernet0/1
Hits: 0 Misses: 0
Expired translations: 0
Dynamic mappings:
-- Inside Source
[Id: 1] access-list 50 pool network1 refcount 0
pool network1: netmask 255.255.255.248
start 85.198.0.1 end 85.198.0.5
type generic, total addresses 5, allocated 0 (0%), misses 0
Overloading NAT ( PAT ) Configuration :
1. On interface that connect to LAN (Local outside interface ) : #ip nat inside
2. On interface that connect to WAN (Global inside interface ) : #ip nat outside
3. #access-list statndard-no permit network wildcard-mask
Router(config)#access-list 50 permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255
4. #ip nat inside source list access-list-no interface interface-name overload
Router(config)#ip nat inside source list 50 interface fastEthernet 0/0 overload
5. #show ip nat statics
Router#show ip nat
*Mar 1 00:07:41.463: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router#show ip nat st
Router#show ip nat statistics
Total active translations: 0 (0 static, 0 dynamic; 0 extended)
Outside interfaces:
FastEthernet0/0
Inside interfaces:
FastEthernet0/1
Hits: 0 Misses: 0
Expired translations: 0
Dynamic mappings:
-- Inside Source
[Id: 1] access-list 50 interface FastEthernet0/0 refcount 0

We must be taking the same course, Accessing the WAN 4.0 from the netacad. Another great article!
ReplyDelete