Router (or switch ) has 3 kind of memory :
- ROM
- FLASH
- NVRam (none Available Ram) : hold the router and switch configuration file.
- When you turn your device on , first a POST (Power on self test ) is run then bootstrap file is run from ROM .
- Bootstrap looks and loads IOS from flash . (IOS is in order place in : Flash , TFTP server , RAM )
- Device copy satrtup.config from NVRAM to RAM
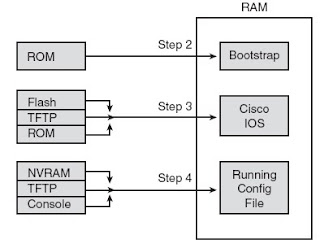
How a Router Chooses Which OS to Load :
A router chooses the OS to load based on the low-order 4 bits in the configuration register
and the details configured in any boot system global configuration commands found in
the startup-config file. The low-order 4 bits (the 4th hex digit) in the configuration register
are called the boot field, with the value of these bits being the first value a router examines
when choosing which OS to try and load. The boot field’s value when the router is powered
on or reloaded tells the router how to proceed with choosing which OS to load.
The process to choose which OS to load, on more modern routers that do not have
an RxBoot OS, happens as follows (note that “boot” refers to the boot field in the
configuration register):
- Step 1 : If boot field = 0, use the ROMMON OS.
- Step 2 :If boot field = 1, load the first IOS file found in Flash memory.
- Step 3 : If boot field = 2-F:
- a. Try each boot system command in the startup-config file, in order, until one works.
- b. If none of the boot system commands work, load the first IOS file found in Flash memory.
NOTE On most Cisco routers, the default configuration register setting is
hexadecimal 2102.
NOTE Cisco represents hexadecimal values by preceding the hex digit(s) with 0x—for
example, 0xA would mean a single hex digit A.


No comments:
Post a Comment